Information About Saigon Eye Hospital – Ngo Gia Tu

Learn about eye examination services at Saigon Eye Hospital – Ngo Gia Tu
At Saigon Eye Hospital – Ngo Gia Tu, a comprehensive eye examination is always the first and most important step. Whether you come for prescription glasses, medical treatment, or refractive surgery consultation, a general eye exam helps doctors accurately assess your vision and overall eye health before recommending further services.
Address: 355 – 365 Ngo Gia Tu, Ward 3, District 10, Ho Chi Minh City
Hotline: 028 3830 0999 – 1900 555553
Working hours:
- Monday – Saturday: 7:30 AM – 4:30 PM
- Sunday: Closed
Patients can schedule an appointment in advance to save waiting time and choose a suitable time slot.
What Does an Eye Examination at Saigon Eye Hospital – Ngo Gia Tu Include?
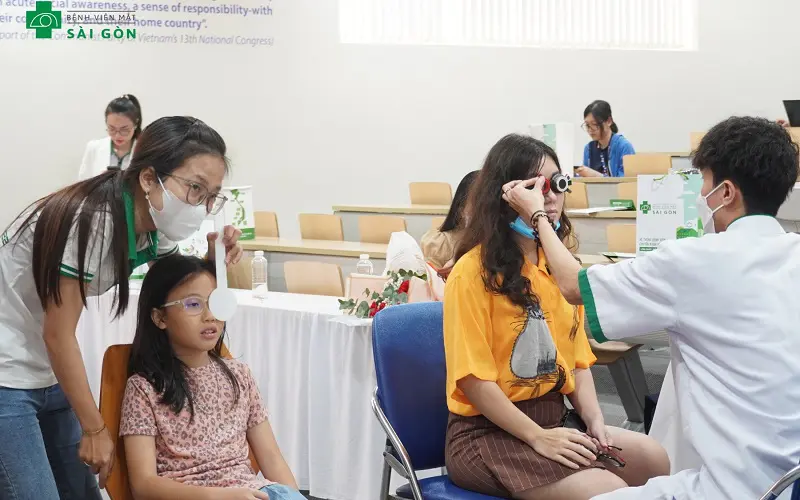

What does an eye examination at Saigon Eye Hospital – Ngo Gia Tu include?
At Saigon Eye Hospital – Ngo Gia Tu, many people often confuse refraction testing with a comprehensive eye exam. In reality, these are two different services.
- Refraction test: Determines whether you have nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism, or presbyopia, and measures your exact prescription.
- Comprehensive eye exam: Includes refraction testing along with multiple in-depth assessments to evaluate overall eye health.
1. Visual Acuity and Refraction Test
The process usually begins with checking visual acuity in each eye. If vision does not reach 10/10, the doctor will perform an automated refraction test combined with trial lenses using a vision chart.
Patients will undergo:
- Measurement with an automated refractometer
- Rechecking using a standard eye chart
- Trial lenses adjusted until the clearest vision is achieved
The results are recorded in the medical file. Based on this, the doctor will advise suitable options: eyeglasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery if the patient qualifies.
2. Comprehensive Eye Health Examination
At Saigon Eye Hospital – Ngo Gia Tu, after refraction testing, the doctor will conduct a full eye health assessment, including: examination of the cornea, conjunctiva, and anterior chamber; intraocular pressure measurement; fundus examination; and evaluation of the lens and retina.
The goal of this step is to detect early signs of underlying conditions such as glaucoma, cataracts, diabetic retinopathy, and macular degeneration. In many cases, patients do not experience obvious symptoms in the early stages, so these conditions can only be identified through a thorough examination.
If necessary, the doctor may recommend additional diagnostic tests.
Common Diagnostic Imaging Tests

Learn about eye examination services at Saigon Eye Hospital – Ngo Gia Tu
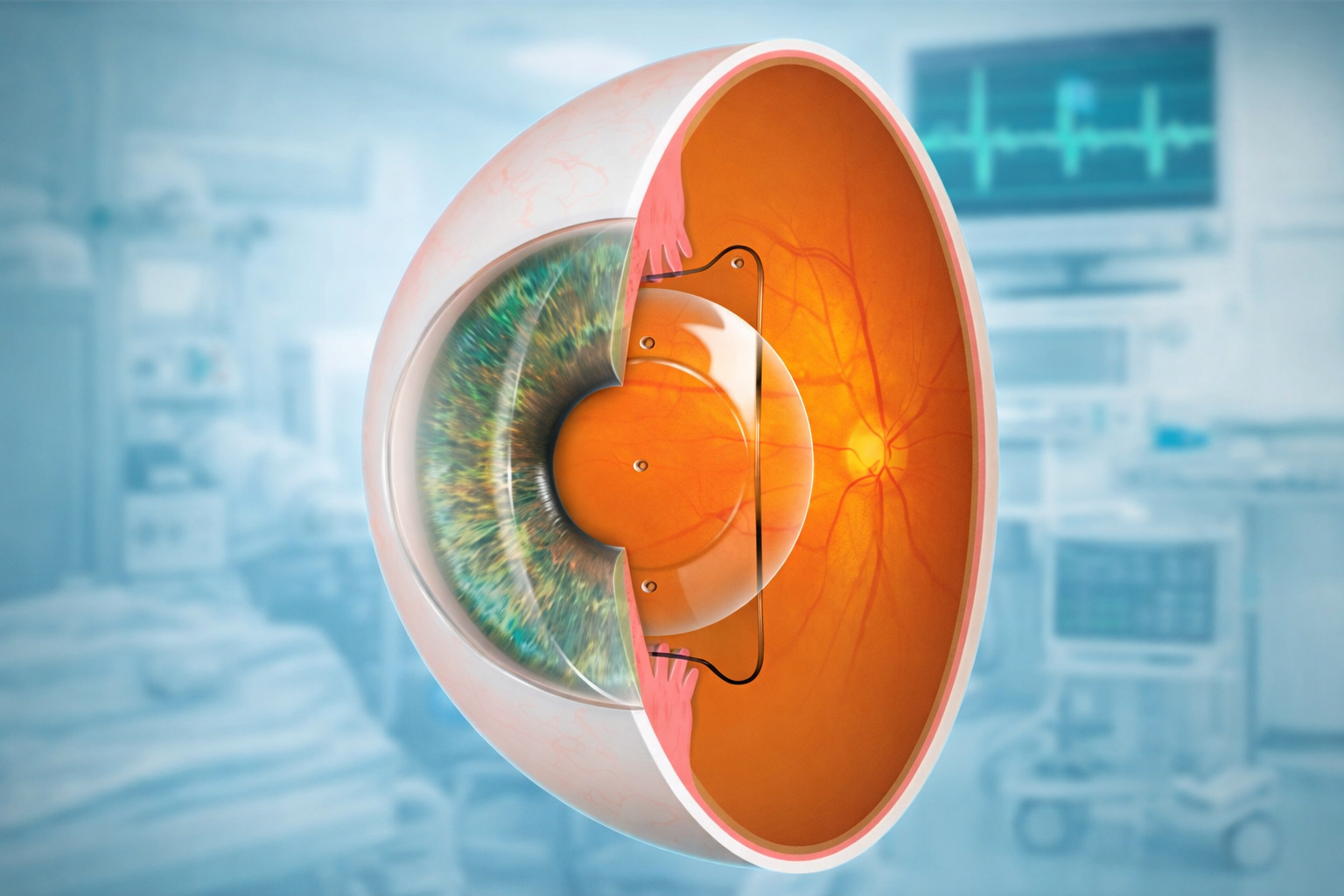
Visual observation alone is not sufficient to assess the entire structure and internal damage of the eye. Therefore, modern imaging techniques may be applied.
OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography)
This is a retinal cross-sectional imaging method that analyzes each layer of nerve tissue at the back of the eye. OCT is particularly useful in diagnosing diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, macular degeneration, macular edema, and more.
OCT images allow doctors to monitor disease progression and evaluate treatment effectiveness.
Fundus Photography
This technique captures images of the retina and optic disc. It helps doctors detect and monitor retinal vascular abnormalities, as well as damage caused by hypertension or diabetes.
Corneal Topography
Corneal topography evaluates the curvature and surface shape of the cornea. This test is important for:
- Diagnosing refractive errors
- Detecting keratoconus
- Screening before refractive surgery
- Pre-operative assessment for cataract surgery
Corneal mapping results help doctors create a safe and appropriate treatment plan.
Ocular Ultrasound
Eye ultrasound is often indicated when the transparent media of the eye is obstructed, for example in cases of advanced cataracts, anterior chamber hemorrhage, or suspected retinal detachment.
This method helps evaluate internal eye structures when direct observation is not possible.
Fluorescein Angiography
This technique examines the retinal blood vessels using contrast dye. Fluorescein angiography helps detect vascular damage, fluid leakage, or retinal ischemia.
Is Regular Eye Examination Necessary?
Many people only visit an eye doctor when experiencing blurred vision or eye pain. However, according to ophthalmologists, regular eye examinations are essential—even when there are no symptoms.
The reason is that many eye diseases progress silently over a long period. For example:
- Glaucoma can damage the optic nerve without causing pain.
- Diabetic retinopathy may not affect vision in its early stages.
- Macular degeneration develops slowly and is difficult to detect early.
Regular check-ups help detect abnormalities early, monitor changes in vision, adjust prescriptions in time, and proactively protect eye health.
Adults should have an eye exam 1–2 times per year. Those with underlying conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or a family history of eye disease should schedule more frequent visits as advised by their doctor.
When Should You See an Eye Doctor Immediately?
In addition to routine check-ups, you should visit an eye hospital immediately if you experience the following symptoms:
- Sudden vision loss
- Blurred or double vision
- Persistent eye pain
- Unusual light sensitivity
- Flashes of light or numerous floaters
- Red, irritated eyes with continuous tearing
These may be signs of serious eye conditions that require prompt treatment.
An eye examination at Saigon Eye Hospital – Ngo Gia Tu is not simply about measuring your prescription; it is a comprehensive evaluation of visual health. From refraction testing and intraocular pressure measurement to advanced imaging diagnostics, each step contributes to an accurate diagnosis and an appropriate treatment plan.

 vi
vi 13-Feb-2026
13-Feb-2026
.svg) Hotline
Hotline Appointment
Appointment https://matsaigonngogiatu.com/
https://matsaigonngogiatu.com/ 355–365 Ngô Gia Tự, P.2, Q.10, Ho Chi Minh City
355–365 Ngô Gia Tự, P.2, Q.10, Ho Chi Minh City Opening Hours
Opening Hours






 0916.741.763
0916.741.763