
How Does Wearing Contact Lenses Overnight Harm Your Eyes?
In today’s fast-paced lifestyle, many people rely on contact lenses as a convenient solution to improve both vision and appearance. However, quite a few individuals, due to fatigue or carelessness, forget to remove their contact lenses before going to sleep. This seemingly minor habit can actually cause serious eye damage and may have long-term effects on vision if repeated frequently. The article below will help you understand why wearing contact lenses overnight is dangerous, the potential complications involved, and how to use contact lenses safely to protect your eyes.
How do your eyes change while you sleep?
When you fall asleep, the physiological activity of your eyes changes significantly. Tear production decreases, the natural cleansing process of the corneal surface slows down, and the amount of oxygen reaching the cornea is lower than when you are awake.
Under normal conditions, the cornea receives oxygen directly from the air. However, when wearing contact lenses, especially during sleep, the lenses act as a barrier, severely limiting the amount of oxygen that reaches the cornea. Prolonged oxygen deprivation can weaken the corneal surface, creating conditions for microscopic damage to develop.
How does wearing contact lenses overnight harm your eyes?
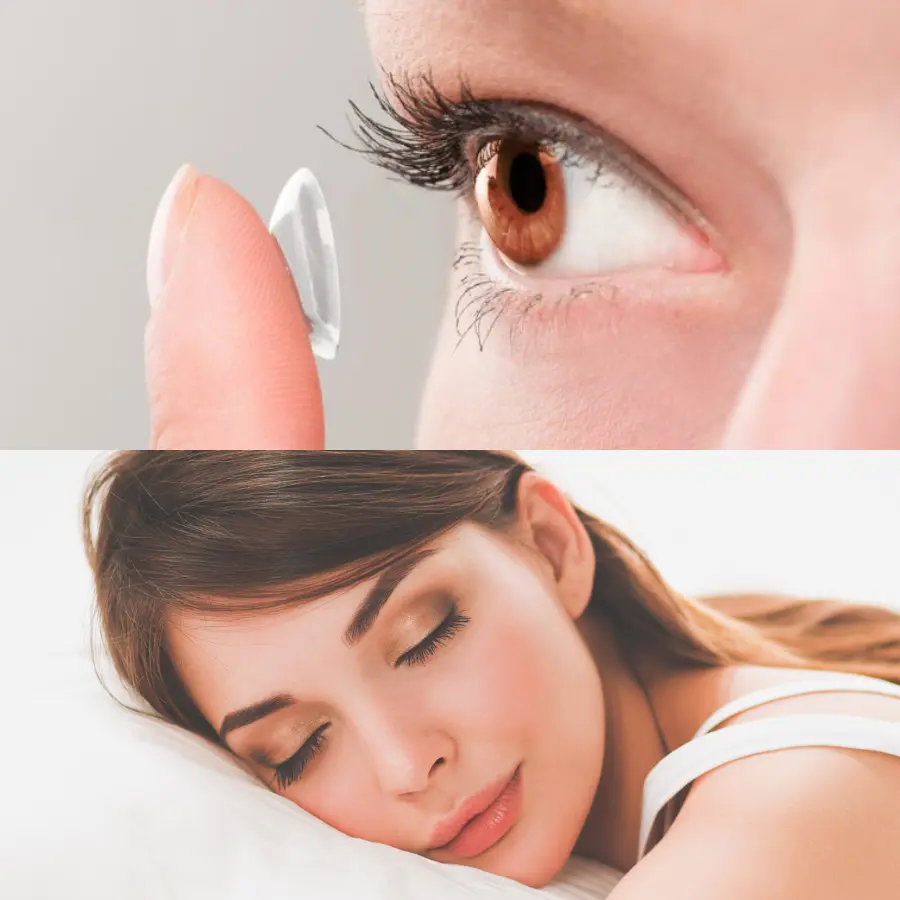
How does wearing contact lenses overnight harm your eyes?
1. Dry eyes and prolonged irritation
Wearing contact lenses while sleeping reduces the natural moisture of the eyes. The lenses can absorb water from the tear film, causing dryness, a gritty sensation, and burning upon waking. If this occurs repeatedly, contact lens wearers may develop chronic dry eye syndrome, leading to persistent discomfort and a reduced quality of daily life.
2. Corneal oxygen deprivation
The cornea is transparent tissue without blood vessels, so it depends entirely on oxygen from the air. When contact lenses are worn overnight, especially lenses not designed for extended wear, the cornea experiences severe oxygen deprivation. As a result, corneal cells become weakened, more prone to shedding, and may develop tiny cracks that are invisible to the naked eye.
3. Increased risk of bacterial keratitis
The closed, moist, and oxygen-poor environment during sleep provides ideal conditions for bacteria to grow on the surface of contact lenses. Once the cornea has been damaged by lack of oxygen, bacteria can easily penetrate and cause keratitis.
What is concerning is that early symptoms are often very mild. Patients may only notice redness, slight itching, or discomfort, which can easily be mistaken for normal eye strain. Many people continue wearing contact lenses, allowing the inflammation to progress rapidly within hours and become severe.
4. Risk of long-term vision damage
Unlike the skin, the eye does not have a strong ability to heal itself completely. Once the cornea is deeply damaged, the risk of corneal scarring is high. Corneal scars can permanently reduce vision, causing blurred vision, glare, or image distortion.
In severe cases, keratitis caused by wearing contact lenses overnight may require intensive treatment or even advanced medical intervention to preserve vision.
Why do many people remain careless about sleeping in contact lenses?
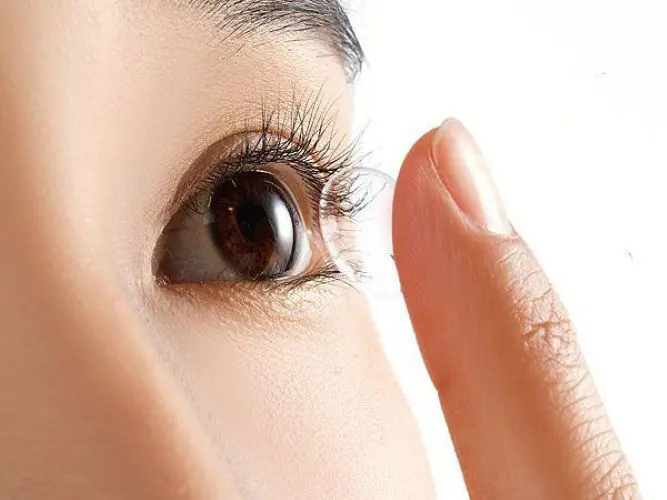
Why do many people remain careless about sleeping in contact lenses?
Many people believe that accidentally sleeping in contact lenses for just one night will not cause any harm. However, it is this repeated habit that poses the real danger. Each time contact lenses are worn overnight, the cornea undergoes another episode of oxygen deprivation and microscopic damage. Over time, these injuries accumulate and significantly increase the risk of complications.
In addition, prolonged use of contact lenses, improper storage, or wearing lenses beyond their recommended replacement schedule further increases the risk of eye infections.
Proper steps to take
If you accidentally fall asleep while wearing contact lenses, it is important not to panic and not to remove the lenses immediately.
- Instill artificial tears to moisten your eyes and the contact lenses
- Gently massage your eyelids to help soften the lenses
- Slowly slide the lenses off the cornea, avoiding sudden pulling
- After removal, allow your eyes to rest and avoid wearing contact lenses for the remainder of the day if possible
If you experience pain, redness, or blurred vision after removing the lenses, you should seek an eye examination promptly.
Golden rules for safe contact lens use
To minimize the risk of complications, contact lens users should follow these essential rules:
- Always remove contact lenses before sleeping
- Wash and thoroughly dry your hands before handling lenses
- Store lenses properly using appropriate contact lens solution, not tap water
- Replace lenses according to the manufacturer’s recommendations
- Avoid exposing contact lenses to pool water or seawater
Following these rules not only reduces the risk of infection but also extends the lifespan of the lenses and protects overall eye health.
Warning signs of eye infection that require immediate medical attention
You should visit an eye care professional as soon as possible if you experience any of the following symptoms after using contact lenses:
- Persistent redness that does not improve after lens removal
- Increasing eye pain or a worsening gritty or burning sensation
- Blurred vision or reduced visual acuity
- Sensitivity to light
- Unusual discharge from the eyes
Early detection and timely treatment are crucial to minimizing the risk of long-term vision damage.
Contact lenses offer many conveniences, but they are only truly safe when used correctly. Wearing contact lenses overnight is a habit that carries significant risks to eye health, from dry eyes and oxygen deprivation to keratitis and serious infections. Proactively removing contact lenses before sleep and practicing proper eye care are simple yet highly effective ways to protect your vision in the long term.

 vi
vi 04-Jan-2026
04-Jan-2026










 0916.741.763
0916.741.763 Appointment
Appointment