What Is Collamer and What Is It Made Of?
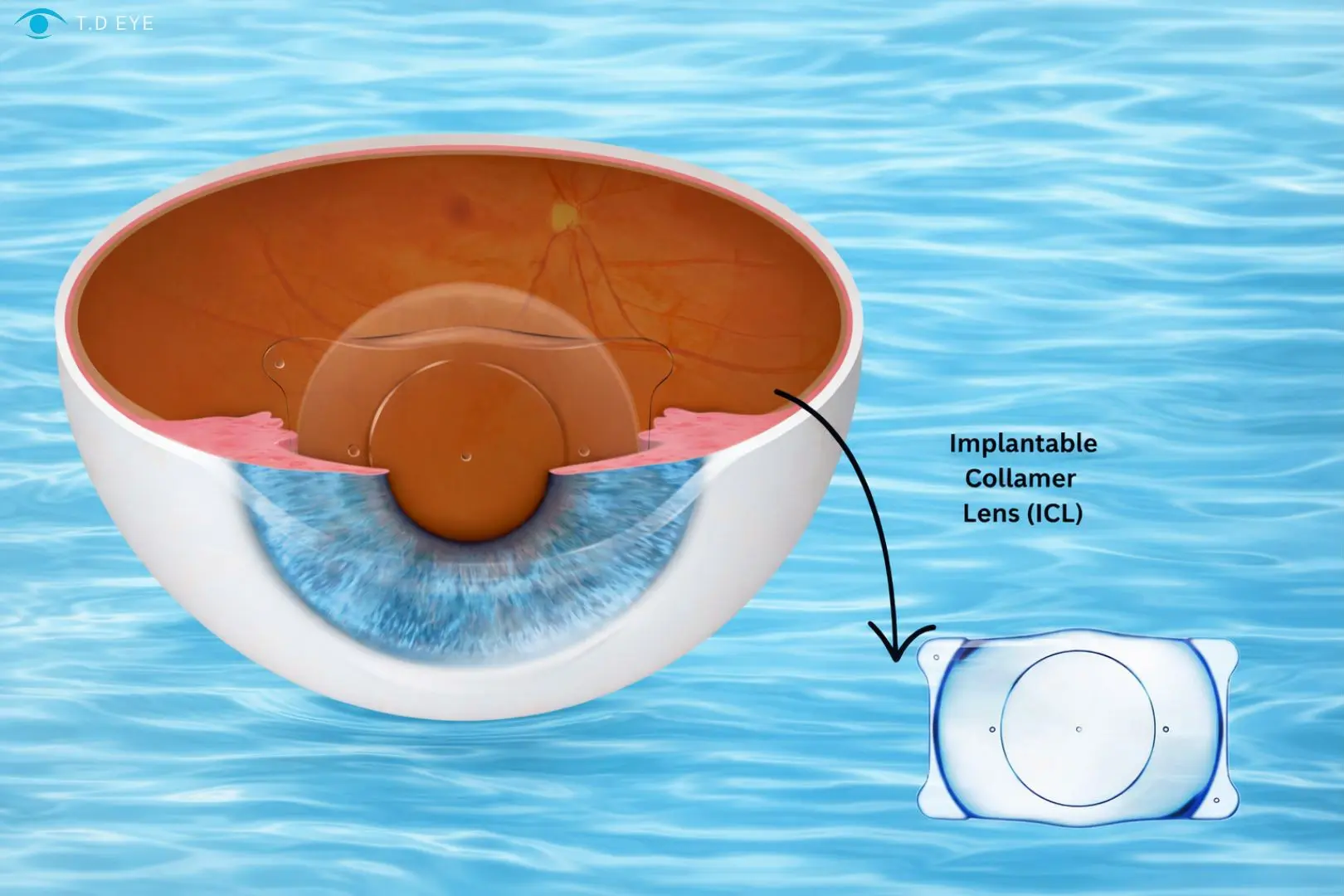
What Is Collamer and What Is It Made Of?
Collamer is a proprietary material used in Phakic ICL, composed of a combination of purified collagen and a biocompatible copolymer, along with water and an ultraviolet light–absorbing agent. The presence of natural collagen in collamer gives this material a very high level of biocompatibility with human ocular tissues, allowing the lens to function harmoniously within the intraocular environment.
Collamer is soft, flexible, and foldable, enabling the lens to be inserted into the eye through a very small microsurgical incision. Once positioned correctly, the lens unfolds naturally and remains stable without causing foreign body sensation or discomfort for the patient. Thanks to its stability and ability to maintain long-term optical clarity, collamer has been widely used in ophthalmology for many years and is highly regarded for its safety profile.
Phakic ICL as a Refractive Error Correction Method
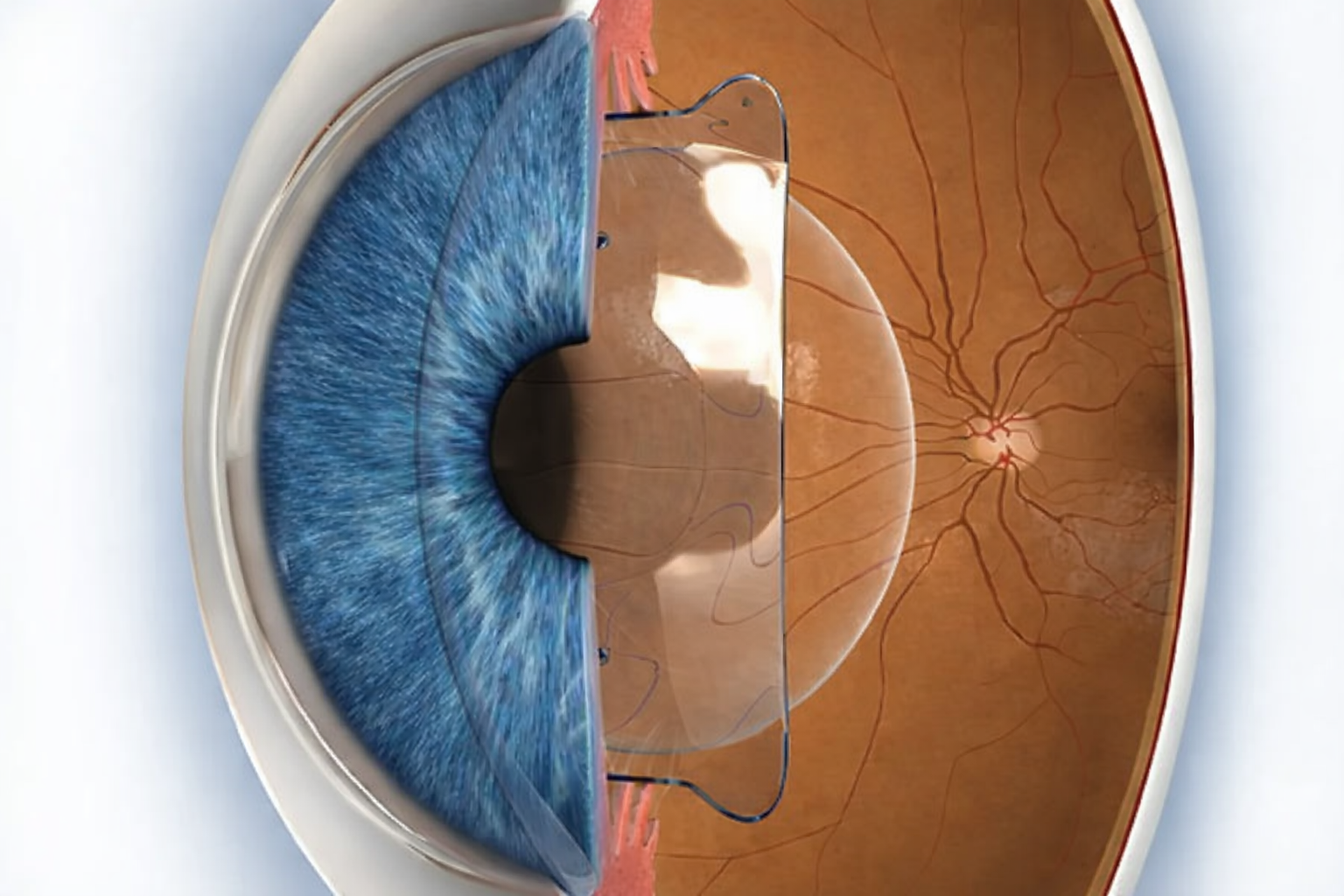
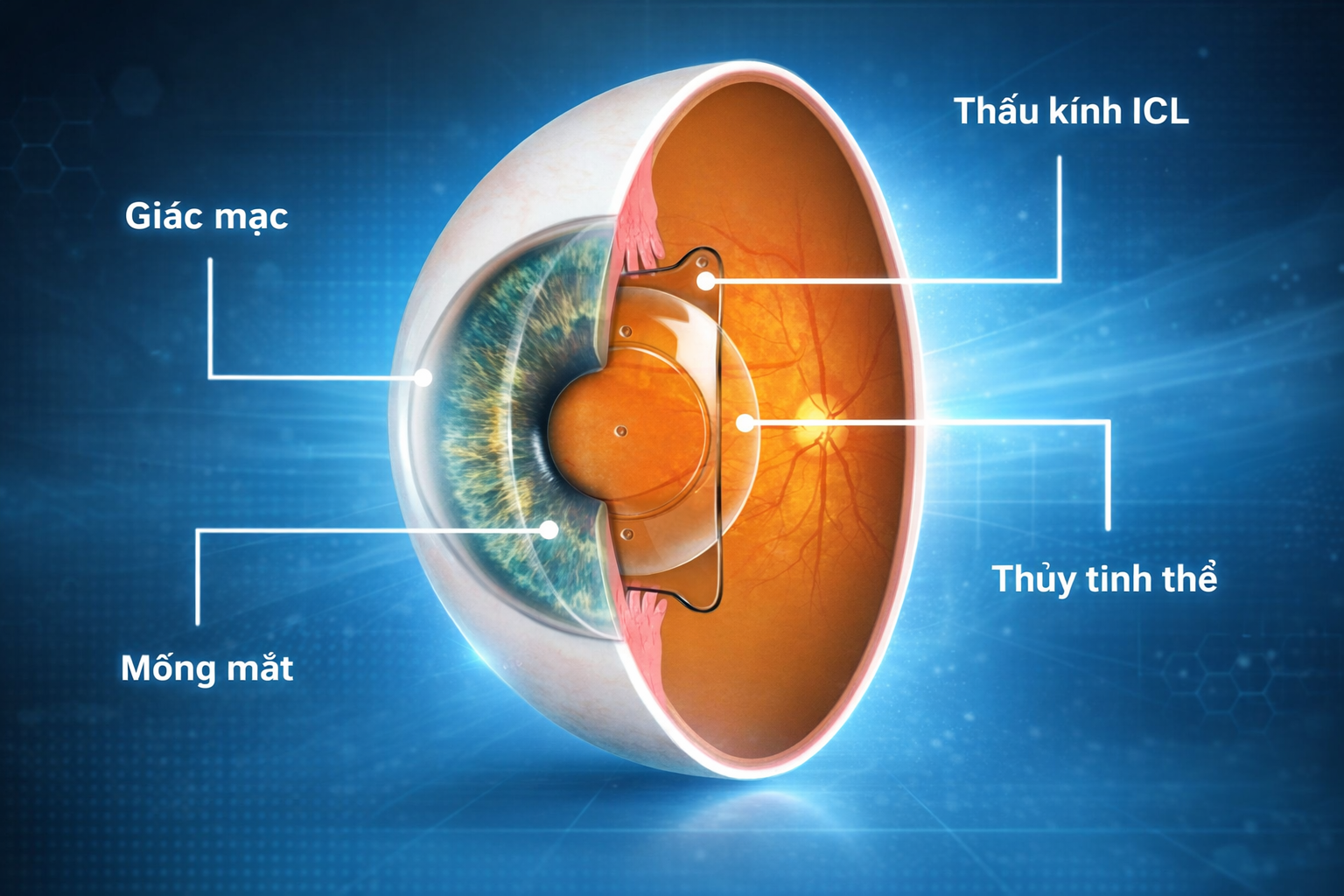
Phakic ICL is an intraocular lens designed to be implanted in the eye without removing the natural crystalline lens. This lens is positioned behind the iris and in front of the crystalline lens, enabling precise correction of refractive errors such as myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism. Unlike laser-based refractive procedures, Phakic ICL does not alter the shape or thickness of the cornea, thereby preserving the eye’s natural anatomical structure.
The key factor that differentiates Phakic ICL and contributes to its effectiveness lies in the material from which the lens is made—collamer. This material forms the scientific foundation that allows the procedure to achieve high biocompatibility and long-term visual stability.
Biocompatibility of Collamer
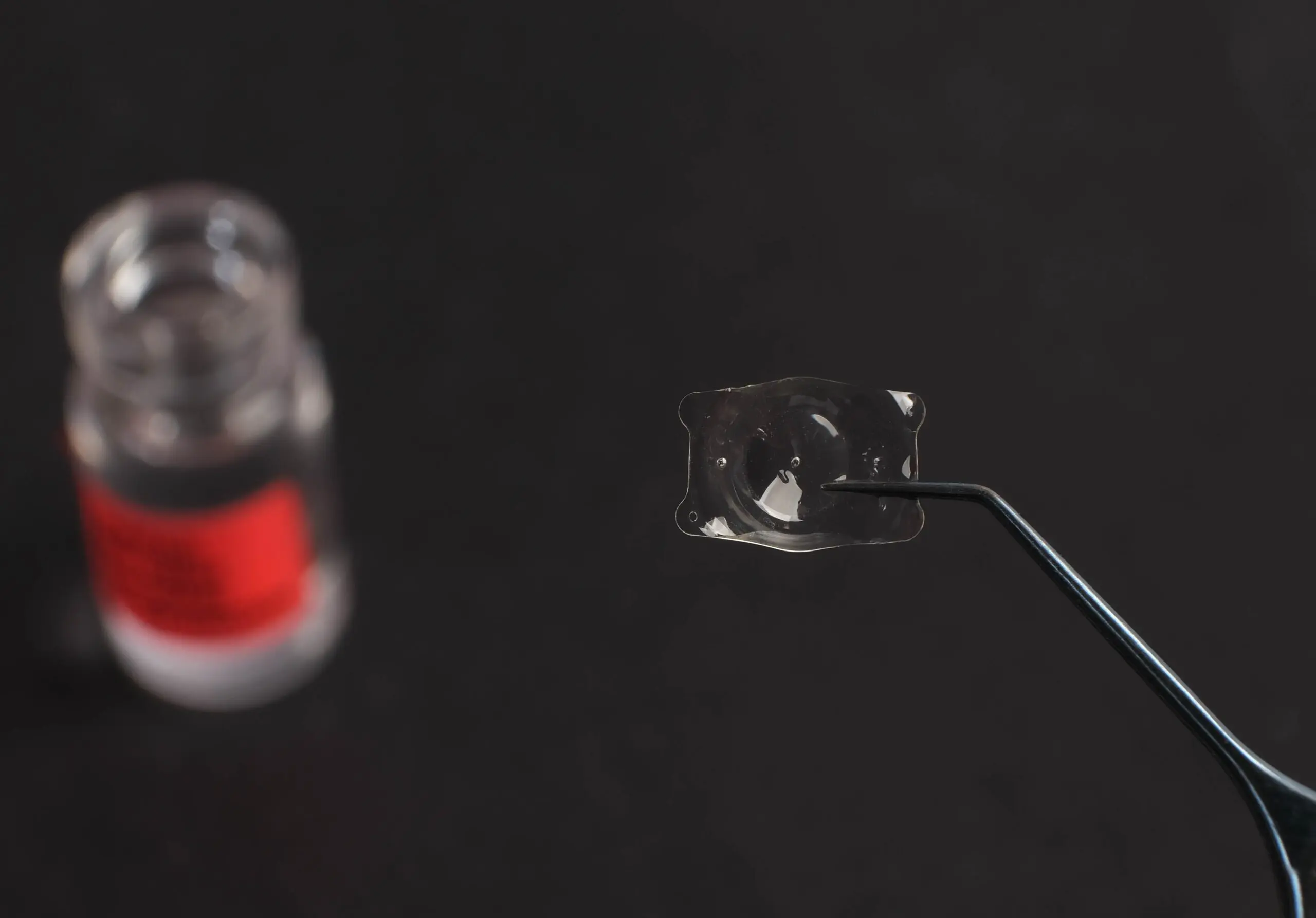

Biocompatibility of Collamer
One of the most remarkable advantages of collamer is its superior level of biocompatibility. The collagen content in collamer attracts fibronectin, a naturally occurring protein that helps form a protective layer on the surface of the lens. This layer limits immune system recognition, thereby reducing the risk of inflammation or adverse reactions following implantation.
In addition, collamer carries a negative ionic charge, which helps repel proteins in the aqueous humor and reduces adhesion and deposition on the lens surface. As a result, the optical clarity of the lens is maintained over time, minimizing the risk of opacification or deterioration in visual quality.
Advantages of Collamer Material in Ophthalmology
Collamer is considered one of the most advanced intraocular lens materials currently available due to its harmonious combination of biological and optical properties.
1. High Biocompatibility
The first and most important advantage of collamer is its exceptionally high level of biocompatibility. By containing purified collagen, a component naturally present in ocular tissues, collamer is well accepted within the intraocular environment, significantly reducing the risk of inflammatory responses or immune reactions after implantation. This is a key factor that allows Phakic ICL to function stably over the long term without causing irritation or discomfort for patients.
2. Softness and Flexibility
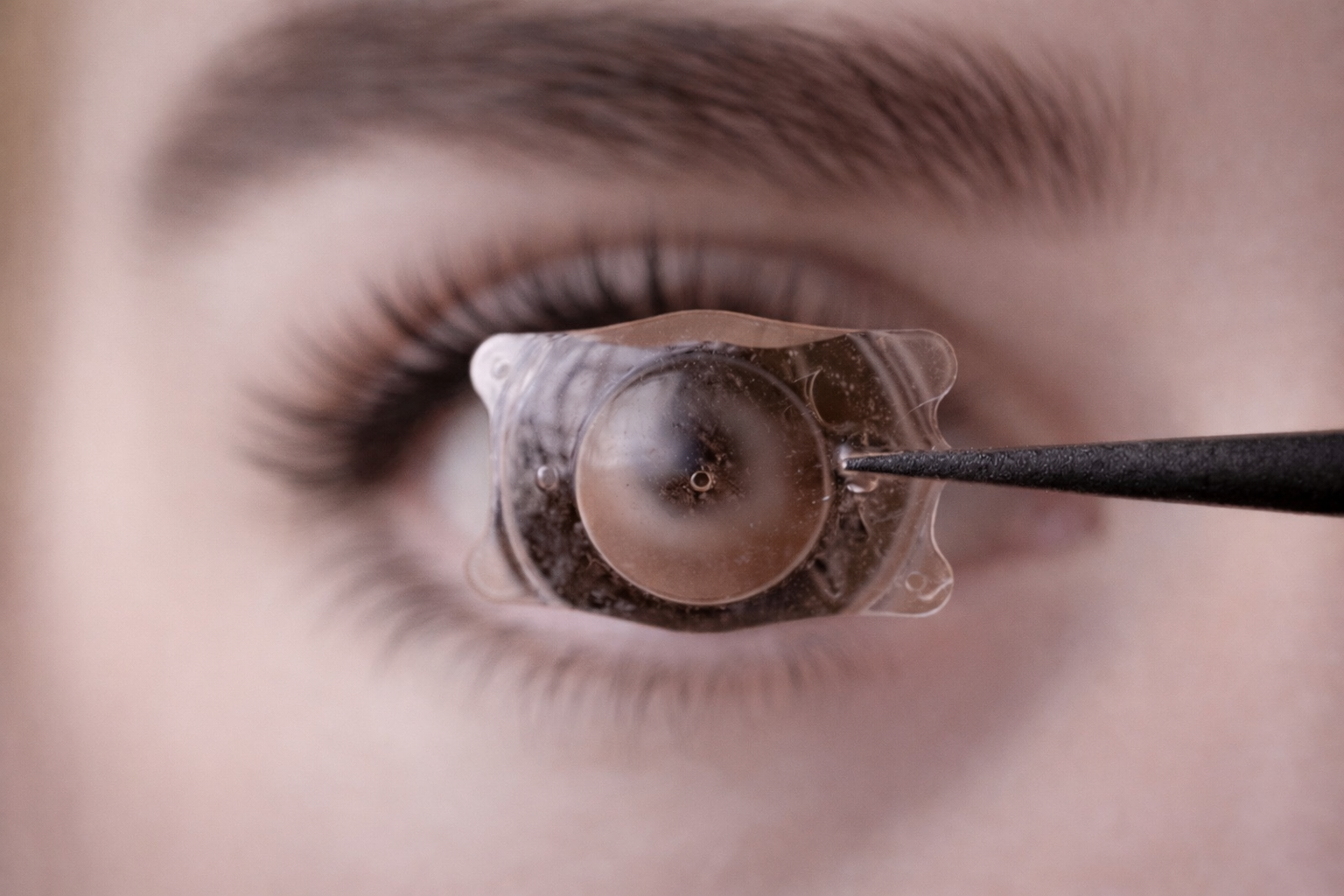
Advantages of Collamer Material in Ophthalmology
Another major advantage of collamer is its softness and flexibility. Unlike stiffer lens materials such as acrylic or silicone, collamer has high elasticity, allowing the lens to be folded and inserted through a very small microsurgical incision. This helps reduce surgical trauma, minimize corneal tissue damage, and shorten postoperative recovery time. At the same time, once properly positioned, the collamer lens maintains stable shape without causing foreign body sensation or interfering with daily activities.
Furthermore, collamer offers significant flexibility in long-term treatment planning. Because Phakic ICL using collamer does not alter corneal structure or remove natural ocular tissue, the lens can be removed in the future if necessary. This preserves future ophthalmic treatment options and provides patients with greater peace of mind when choosing a long-term refractive correction method.
3. Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
From an optical standpoint, collamer provides high transparency and optimal light transmission. This material helps reduce unwanted light scattering and reflection, thereby improving visual quality, especially in low-light conditions or at night. Numerous clinical studies have shown that lenses made from collamer deliver sharper images, better contrast sensitivity, and a more natural visual experience compared to some earlier intraocular lens materials.
Collamer also effectively resists protein deposition due to its negative ionic charge. This property repels proteins in the aqueous humor, limiting their adhesion to the lens surface and maintaining long-term optical clarity. This is an important advantage in reducing the risk of lens opacification and ensuring stable visual quality over time.
4. UV Protection
Another notable benefit of collamer is its ability to incorporate an ultraviolet filter. Collamer lenses can absorb a portion of harmful UV radiation before light penetrates deeper into intraocular structures, helping protect the retina and crystalline lens from long-term ultraviolet damage. This feature is particularly valuable for patients living or working in environments with high levels of sunlight exposure.
The Role of Collamer in Phakic ICL
Beyond its biological safety, collamer plays a critical role in enhancing visual quality. Collamer lenses offer high transparency, allowing light to enter the eye efficiently while reducing unwanted reflections. This results in clearer vision, especially under low-light or nighttime conditions.
In addition, collamer integrates a UV-filtering component that helps protect intraocular structures from long-term ultraviolet exposure. This is an important factor in reducing the risk of retinal damage and limiting the development of cataracts in the future.
A major advantage of Phakic ICL using collamer is its ability to fully preserve the cornea. Because it does not require corneal reshaping as laser-based procedures do, Phakic ICL is particularly suitable for patients with thin corneas, dry eye, or those who do not meet the criteria for laser refractive surgery. Preserving corneal structure helps maintain the eye’s natural physiology and reduces the risk of long-term complications.
Clinical Applications and Flexibility of Phakic ICL
Phakic ICL made with collamer is commonly indicated for patients with moderate to high refractive errors, stable vision, and no serious ocular diseases. The lens is custom-designed for each eye based on precise measurements, optimizing refractive correction outcomes.
Notably, Phakic ICL can be removed if necessary, such as in cases of significant vision changes or when other ophthalmic treatments are required. This flexibility provides reassurance for patients and allows access to future advancements in vision correction technology.
With its high biocompatibility, ability to maintain long-term optical clarity, and role in preserving corneal structure, collamer has helped establish Phakic ICL as a safe and effective refractive correction solution for many patients. However, to achieve optimal outcomes, thorough evaluation and surgical procedures should be performed by experienced ophthalmologists using advanced technology. When properly indicated, Phakic ICL with collamer can deliver stable, clear, and long-lasting vision.

 vi
vi 27-Jan-2026
27-Jan-2026








 0916.741.763
0916.741.763 Appointment
Appointment